Đọc hiểu chi tiết Đáp án Đề thi vào 10 Chuyên Anh Đồng Nai 2021-2022 mới nhất từ Sprout From Ground, dành cho các bạn đang luyện thi chuyên vào 10.

A. Phân tích Đáp án Đề thi Vào 10 Chuyên Anh Đồng Nai 2021-2022
I. PHONOLOGY
For questions 1-5, choose the letter (A, B, C or D) to indicate the word whose underlined part is pronounced differently from that of the others. (0.5 point)
1. A. exhibition B. exhaustion C. honorable D. rehearsal
| /,eksi’bi∫n/ /ig’zɔ:stid/ /’ɔnərəbl/ /ri’hə:sl/ |
2. A. obstacle B. observant C. obsolete D. obvious
| /’ɒbstəkl/ /əb’zə:vənt/ /’ɒbsəli:t/ /’ɒbviəs/ |
3. A. conservation B. preservation C. conversation D. transportation
| /,kɔnsə:’vei∫n/ /,prezə’vei∫n/ /,kɔnvə’sei∫n/ /trænspɔ:’tei∫n/ |
4. A. bury B. justice C. lullaby D. cultivate
| /’beri/ /’dʒʌstis/ /’lʌləbai/ /’kʌltiveit/ |
5. A. loathe B. oatmeal C. oasis D. soap
| /ləʊð/ /ˈəʊt.miːl/ /əʊˈeɪ.sɪs/ /səʊp/ |
For questions 6-10, choose the letter (A, B, C or D) to indicate the word whose main stress is placed differently from that of the others. (0.5 point)
6. A. ,exis,tential B. ,ado’escent C. ,indi’vidual D. fa’cility
7. A. mu’seum B. ca’thedral C. ,sky’scraper D. pro’hibit
8. A. ,down’town B. ‘wander C. ‘treasure D. ‘vendor
9. A. ,intro’duce B. ,volun’teer C. in’terpret D. enter’tain
10. A. ‘admirable B. ‘preferable C. ‘pain,stakingly D. ,hori’zontal
II. LEXICO-GRAMMAR
Part 1: Questions 11-20 (1.0 point)
Choose the correct answer (A, B, C, D) to each of the following questions.
11. He became internationally famous _______ his novels.
A. with
B. for
C. about
D. at
| be famous for: nổi tiếng vì cái gì |
12. It is strongly recommended that the machines ______ every year.
A. should check
B. were checked
C. be checked
D. check
| Subjective: It is recommended/suggested/… that + S + (should) + Vinfi Bị động: be + PII => be checked: được kiểm tra |
13._______ you to change your mind, you’d be welcomed to join our staff.
A. If
B. Unless
C. Were
D. Had
| Đảo ngữ với câu điều kiện loại 2:Were + S + to V, S + would + Vinfi |
14. Jack says he appreciates ______ out last weekend.
A. your help
B. helping him
C. your helping him
D. to be help
| appreciate + tính từ sở hữu + Ving: đề cao |
15. The first meeting was a success, so we ______ a second one.
A. needn’t have hold
B. needed to hold
C. needed hold
D. didn’t need to hold
| didn’t need to do mang ý nghĩa không cần phải làm gì và việc không cần đó đã được biết tới tại thời điểm nói. needn’t have done được sử dụng khi một việc đáng lẽ ra không cần thiết phải làm nhưng thực tế đã được thực hiện (trong quá khứ) |
16. It’s no ______ having to work in the same office as hers. You have to watch your words all the time.
A. harm
B. wonder
C. use
D. joke
| It’s no use/no good + Ving: làm gì vô ích, không có tác dụng |
17. Uncle Ross is a ______ smoker. He smokes 2 packets a day.
A. habitual
B. continual
C. frequent
D. permanent
| habitual: luôn luôn làm điều gì đó như một thói quen; quen thói; thường xuyên (thường dùng với các từ tiêu cực như drug use, liar, drunkard, thief, meanness, criminals, …) |
18. The thief ____ unnoticed as he left the building.
A. looked
B. seemed
C. went
D. made
| go unnoticed: không bị nhìn thấy, không bị để ý |
19. She fell down a ________ of stairs and hurt her back.
A. group
B. flight
C. lump
D. case
| a flight/set of stairs: cầu thang (số nhiều) |
20. People in the village have got an _____appetite for news.
A. inexorable
B. inevitable
C. insatiable
D. inedible
| inexorable: không lay chuyển được, không động tâm, không mủi lòng inevitable: không thể tránh được, chắc chắn xảy ra insatiable: không thể thoả mãn được => have an insatiable appetite/desire/hunger for: có khao khát vô độ inedible: không ăn được |
Part 2: Questions 21-30 (1.0 point)
Fill in each blank with the correct form of the word in brackets.
21. Lowering interest rates could have ____disastrous_____ consequences for the economy. (DISASTER)
| disaster (N): thảm họa => disastrous (a): thảm khốc: a +N Dịch: Hạ lãi suất có thể gây ra những hậu quả tai hại cho nền kinh tế |
22. All the doctors and nurses have been ___vaccinated______ against the COVID-19.(VACCINE)
| vaccine (N): vacxin -> vaccinate (V): tiêm vacxin: Bị động Dịch: Tất cả bác sĩ và y tá đã được tiêm vaccine chống COVID-19. |
23. The equator is a(n) ___imaginary______line around the middle of the earth. (IMAGINE)
| imagine (V): tưởng tượng -> imaginary (a): tưởng tượng, không có thực, ảo Dịch: Đường xích đạo là một đường tưởng tượng danh trung tâm của Trái Đất |
24. Gwen was a boring, ____humourless_____ woman who never laughed. (HUMOR)
| humor (N): khiếu hài hước => humorless (a): không có tính cách hài hước Dịch: Gwen là một cô gái nhàm chán, không hài hước mà không bao giờ cười |
25. The whole town is in ____festive_____ mood. (FESTIVAL)
| festival (N): lễ hội -> festive (a): ngày hội Dịch: Cả thành phố ở trong tâm trạng/không khí lễ hội |
26. They fought a long battle against prejudice and ___ignorance___(IGNORE)
| ignore (V): lờ đi -> ignorance (N): sự ngu dốt, sự không biết Dịch: Họ đã chiến đấu một trận chiến lâu dài chống lại định kiến và sự thiếu hiểu biết |
27. He felt that he was being __pressurized___ to resign. (PRESSURE)
| pressure (N): áp lực -> pressurise (V): gây áp lực Dịch: Anh ta cảm thấy rằng mình bị gây áp lực đê thôi việc |
28. One of the ___products______ of unemployment is an increase in crime. (PRODUCE)
| produce (V): sản xuất -> product (N): sản phẩm Dịch: Một trong những sản phẩm của nạn thất nghiệp là sự gia tăng tội phạm |
29. The __advisory_______ board has decided against implementing the new system. (ADVISE)
| advise (V): khuyên -> advisory board: Ban Cố vấn (an advisory board/panel/committee) Dịch: Ban cố vấn đã quyết định không triển khai hệ thống mới |
30. If a feeling or idea __enslaves_______ someone, it influences everything they do or think. (SLAVE)
| slave (N): nô lệ -> enslave (V): chi phối, biến thành nô lệ Dịch: Nếu một cảm giác hoặc ý tưởng chi phối ai đó, nó sẽ ảnh hưởng đến mọi thứ họ làm hoặc suy nghĩ. |
Part 3: Questions 31-35 (0.5 point)
Complete each sentence with the correct form of one of the phrasal verbs made from one word from each box below. Each word is used once only.
| set fall look break pull |
| through after for in off |
31. Who’s going to _____look after______ the children while you’re away?
| look after: trông nom, chăm sóc |
32. We had our house ____broken in_______ last week.
| break in: đột nhập |
33. They ___set off________ for Paris at midnight.
| set off: bắt đầu lên đường |
34. She was so beautiful that he _____fall for______ her as soon as he saw her.
| fall for sb: phải lòng ai |
35. Although he’s in a critical state after the accident, the doctors think he’ll __pull through__.
| pull through: vượt qua (bệnh tật, khó khăn) |
Part 4: Questions 36-40 (0.5 point)
The passage below contains 5 mistakes. For questions 36-40, identify the mistakes and write the line numbers, the incorrect words and the corrections in the blanks provided below the passage. (0) has been done as an example.
NATIONAL PARKS
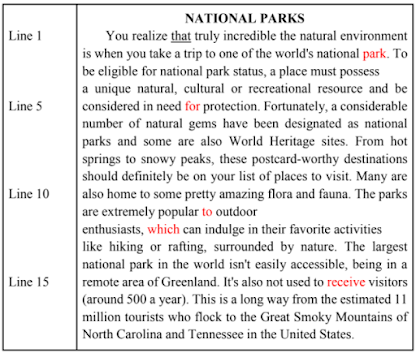
You realize that truly incredible the natural environment is when you take a trip to one of the world’s national park. To be eligible for national park status, a place must possess a unique natural, cultural or recreational resource and be considered in need for protection. Fortunately, a considerable number of natural gems have been designated as national parks and some are also World Heritage sites. From hot springs to snowy peaks, these postcard-worthy destinations should definitely be on your list of places to visit. Many are also home to some pretty amazing flora and fauna. The parks are extremely popular to outdoor enthusiasts, which can indulge in their favorite activities like hiking or rafting, surrounded by nature. The largest national park in the world isn’t easily accessible, being in a remote area of Greenland. It’s also not used to receive visitors (around 500 a year). This is a long way from the estimated 11 million tourists who flock to the Great Smoky Mountains of North Carolina and Tennessee in the United States.
Example:
(0) Line 1: that -> how
Your answers:
36. Line __2_____: …park -> parks…………………….
| one of the world’s national parks: một trong số những công viên quốc gia trên thế giới |
37. Line __5_____: …for -> of…………………….
| be in need of sth: cần cái gì |
38. Line __11_____: …to -> with…………………….
| be popular with sb: được ai ưa chuộng, ngưỡng mộ |
39. Line __12_____: …which -> who…………………….
| Mệnh đề quan hệ: who + V dành cho người do để chỉ cho “outdoor enthusiasts – những người đam mê ngoài trời” ở vế trước |
40. Line __15_____: …receive -> receiving…………………….
| be used to + Ving: quen với điều gì ở hiện tại |
III. READING
Part 1: Questions 41-48 (0.8 point)
Choose the answer (A, B, C or D) that best fits each space.
THE IDEAL JOB
A government research agency recently (41) __ out a survey in which 15,000 people in the UK were asked the question: “What would be your ideal job?” Incredibly, around 60% of those who filled in the questionnaire gave the same answer. It may (42) ___ as a surprise to anyone who actually works in the business, but these people all thought they would like to be writers. (43) ______ no data is available to (44) ___ their reasons for choosing this particular occupation, it seems that what (45) ___ to these people is the lifestyle that they imagine a writer leading Writing work is often done from home, with no (46) ___ timetable and so can be combined with family commitments and other activities. In reality, of course, the lifestyle isn’t so glamorous. Most writers work on a freelance (47) __ and so have no regular salary to rely on, challenging deadlines are the norm, and only the most successful of them can expect to (48) __ a living from it.
41. A. managed B. carried C. arranged D. organized
| carry out (a survey, research, test, …): thực hiện |
42. A. come B. sound C. result D. seem
| come as a surprise: bất ngờ, ngạc nhiên |
43. A. However B. Although C. Otherwise D. Despite
| However, S + V: Tuy nhiên Although + S + V, S + V: Mặc dù Otherwise, S + V: Nếu không thì Despite + N: Mặc dù |
44. A. account B. inform C. explain D. refer
| explain the reasons: giải thích lí do |
45. A. likes B. attracts C. enjoys D. appeals
| appeal to sb for sth: yêu cầu khẩn khoản |
46. A. heavy B. stuck C. fixed D. solid
| heavy: nặng stuck: bị tắc fixed: cố định solid: chắc chắn, liên tục, không nghỉ, không ngắt giữa chừng |
47. A. basis B. method C. system D. way
| work on a freelance basis: làm việc tự do |
48. A. take B. do C. have D. make
| make a living from: kiếm tiền từ cái gì |
Part 2: Questions 49-55 (0.7 point)
Fill each of the following numbered blanks with ONE suitable word.
TREES
All over the world, forests are safeguarding the health of the planet itself. They do this (49) _by__ protecting the soil, providing water and regulating the climate. Trees bind soil to mountain-sides. Hills where the trees have been felled lose 500 times as much soil a year as those with trees.
Trees catch and store rainwater. Their leaves break the impact of the rains, robbing them (50) _of_ their destructive power. The roots of trees allow the water to go into the soil, which gradually releases it to flow down rivers and refill ground-water reserves. Where there are (51) _no_ trees, the rains run in sheets of water off the land, carrying soil with them. Land covered with trees and other plants absorbs 20 times more rainwater than bare earth. As (52) _they_ grow, trees absorb carbon dioxide, the main cause of the “greenhouse effect”, (53) _which__ threatens irreversibly to change the world’s climate. Together, the world’s trees, plants and soils contain three times as much carbon as there is in the atmosphere.
The world’s forests contain (54) _the_ vast majority of its animal and plant species. The tropical rainforests alone have well (55) _over_ half of them, even though they cover only about 6% of the Earth’s land surface.
| 49. by: bằng cách Họ làm điều này bằng cách bảo vệ đất, cung cấp nước và điều hòa khí hậu 50. rob sb of sth: cướp đoạt (lấy trộm) của ai cái gì 51. no: không Where there are no trees: Nơi không có cây nào 52. As + S + V: Khi 53. Mệnh đề quan hệ: which + V để chỉ vật “greenhouse effects” 54. the vast majority of: đại đa số 55. over: quá |
Part 3: Questions 56-62 (0.7 point)
You are going to read an extract from an article about space tourism. Choose from the list A-H the sentence which best summarizes each part (56-62) of the extract. There is one extra sentence which you do not need to use.
A. Careers can be planned in readiness for jobs in space tourism. 58
| So you can start university studies and try to get the sort of work experience |
B. We can look forward to a time of widespread space tourism. 60
| It is possible to envisage a future … from thousands … to hundreds of thousands per year |
C. Individuals can contribute in various ways to making space tourism a reality. 62
| It is possible to take an active role … asking airlines … |
D. The development of space tourism will depend on the level of commercial investment
E. Financial planning is required now if you want to be a space tourist in the future. 57
| the first thing you should do if you want to go to space is save up |
F. There are good reasons for encouraging space tourism. 59
| such tourism is …. the quickest way to start to use the limitless resources of space to solve our problems on Earth |
G. In its initial phase, space tourism will offer only basic facilities. 61
| nearer to “adventure travel” than to a luxury-style hotel |
H. Space tourism is becoming the concern of private companies. 56
| commercial space tourism services is a realistic target for businesses today |
SPACE TOURISM
The idea of what’s called Space Tourism, where ordinary members of the public queue up to buy tickets for travel into outer space and back, really stretches the imagination. According to Alan Grant, this distant dream could soon be a reality…
| 56. | H |
On Earth, governments provide a number of services, such as defence, police and a legal system. But most activities are done by individuals and companies and it is going to be the same in space. Over the past few years a growing volume of work has been done on the subject and it is now clear that setting up commercial space tourism services is a realistic target for businesses today.
| 57. | E |
Many people still think that to get the chance to go to space you have got to try to become an astronaut. Unfortunately, the chances of succeeding are tiny, simply because there are so few astronauts – and there is no prospect of a lot more being employed. However, you need not despair because you will be able to go as a visitor. So for anyone, the first thing you should do if you want to go to space is save up because the demand is expected to be strong and, in the early stages, prices will be high.
| 58. | A |
In order to stay longer in space, you could work in one of the businesses that will be set up in orbit. There will be opportunities in manufacturing – aerospace vehicle makers, orbital construction, electric power, extra-terrestrial mining, chemical engineering and other fields. So you can start university studies and try to get the sort of work experience that will ensure you are well-placed to apply for a job in any of these areas.
| 59. | F |
The general public are very interested in travelling to space. Apart from the interest factor, such tourism is the only way in which space activities can become profitable and the quickest way to start to use the limitless resources of space to solve our problems on Earth. And living in space involves every line of business, from construction to marketing, fashion, interior design and law.
| 60. | B |
It is possible to envisage a future when demand for space tourism travel will grow from thousands of passengers per year to hundreds of thousands per year. Tickets to orbit will cost less and flights will depart from many different airports. Orbital facilities will grow from just being prefabricated modules to large structures constructed for hundreds of guests.
| 61. | G |
But like any other business, space tourism will develop progressively. Starting as a relatively small- scale and relatively high-priced activity. Customers will find that the service will be nearer to “adventure travel” than to a luxury-style hotel. Orbital accommodation will be safe but rather simple. This will be a time for the pioneers who will not mind the jack of comfort.
| 62. | C |
Few projects are successfully completed without the help of people who believe in them. It is possible to take an active role in bringing space tourism about by asking airlines, hotels and travel companies if and when they intend to offer space travel. Others may prefer to lend a hand by doing research into one or more of the areas needing it, or by joining one of the many companies that are already working towards a future in space.
Part 4: Questions 63-70 (0.8 point)
Read the following passage carefully and answer the question 63-70.
IS THERE MORE TO VIDEO GAME THAN PEOPLE REALIZE?
1. Many people who spend a lot of time playing video games insist that they have helped them in areas like confidence-building, presentation skills and debating. Yet this way of thinking about video games can be found almost nowhere within the mainstream media, which still tend to treat games as an odd mix of the slightly menacing and the alien. This lack of awareness has become increasingly inappropriate, as video games and the culture that surrounds them have become very big business indeed.
2. Recently, the British government released the Byron report into the effects of electronic media on children. Its conclusions set out a clear, rational basis for exploring the regulation of video games. The ensuing debate, however, has descended into the same old squabbling between partisan factions: the preachers of mental and moral decline, and the innovative game designers. In between are the gamers, busily buying and playing while nonsense is talked over their heads.
3. Susan Greenfield, renowned neuroscientist, outlines her concerns in a new book. Every individual’s mind is the product of a brain that has been personalized by the sum total of their experiences; with an increasing quantity of our experiences from very early childhood taking place “on screen” rather than in the world, there is potentially a profound shift in the way children’s minds work. She suggests that the fast- paced, second-hand experiences created by video games and the Internet may inculcate a worldview that is less empathetic, more risk-taking and less contemplative than what we tend to think of as healthy.
4. Adam Martin, a lead programmer for an online games developer, says: “Computer games teach and people don’t even notice they’re being taught.” But isn’t the kind of learning that goes on in games rather narrow? “A large part of the addictiveness of games does come from the fact that as you play you are mastering a set of challenges. But humanity’s larger understanding of the world comes primarily through communication and experimentation, through answering the question “What if?” Games excel at teaching this too.”
5. Steven Johnson’s thesis is not that electronic games constitute a great, popular art, but that the mean level of mass culture has been demanding steadily more intellectual engagement from consumers. Games, he points out, generate satisfaction via the complexity of their virtual worlds, not by their robotic predictability. Testing the nature and limits of the laws of such imaginary worlds has more in common with scientific methods than with a pointless addiction, while the complexity of the problems children encounter within games exceeds that of anything they might find at school.
6. Greenfield argues that there are ways of thinking that playing video games simply cannot teach. She has a point. We should never forget, for instance, the unique ability of books to engage and expand the human imagination, and to give us the means of more fully expressing our situations in the world. Intriguingly, the video games industry is now growing in ways that have more in common with an old- fashioned world of companionable pastimes than with a cyber-future of lonely, isolated obsessives. Games in which friends and relations gather round a console to compete at activities are growing in popularity. The agenda is increasingly being set by the concerns of mainstream consumers – what they consider acceptable for their children, what they want to play at parties and across generations.
7. These trends embody a familiar but important truth: games are human products, and lie within our control. This doesn’t mean we yet control or understand them fully, but it should remind us that there is nothing inevitable or incomprehensible about them. No matter how deeply it may be felt, instinctive fear is an inappropriate response to technology of any kind.
8. So far, the dire predictions many traditionalists have made about the death” of old-fashioned narratives and imaginative thought at the hands of video games cannot be upheld. Television and cinema may be suffering, economically, at the hands of interactive media. But literacy standards have failed to decline. Young people still enjoy sport, going out and listening to music. And most research – including a recent $1.5m study funded by the US government – suggests that even preteens are not in the habit of blurring game worlds and real worlds.
9. The sheer pace and scale of the changes we face, however, leave little room for complacency. Richard Bartle, a British writer and game researcher, says. “Times change: accept it; embrace it.” Just as, today, we have no living memories of a time before radio, we will soon live in a world in which no one living experienced growing up without computers. It is for this reason that we must try to examine what we stand to lose and gain, before it is too late.
Questions 63-67: Do the following statements agree with the views of the writer in the reading passage?
On your answer sheet, write:
Y if the statement agrees with the views of the writer.
N if the statement contradicts the views of the writer.
NG if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this.
63. Much media comment ignores the positive impacts that video games can have on many people’s lives. Y
| Yet this way of thinking about video games can be found almost nowhere within the mainstream media, which still tend to treat games as an odd mix of the slightly menacing and the alien |
64. The publication of the Byron Report was followed by a worthwhile discussion between those for and against video games. N
| Recently, the British government released the Byron report into the effects of electronic media on children. |
65. Susan Greenfield’s way of writing has become more complex over the years. NG
| Dịch: Cách viết của Susan Greenfield đã trở nên phức tạp hơn trong những năm qua => Không liên quan vì bài này là về video games và các quan điểm xung quanh nó, chứ không liên quan đến cách viết |
66. More sociable games are being brought out to satisfy the demands of the buying public. Y
| Games in which friends and relations gather round a console to compete at activities are growing in popularity. |
67. Being afraid of technological advances is a justifiable reaction. N
| instinctive fear is an inappropriate response to technology of any kind. |
Questions 68-70: Choose the correct letter, A, B, C or D. Write the correct letter, A-D, on your answer sheet.
68. What main point does Adam Martin make about video games?
A. People are learning how to avoid becoming addicted to them.
B. They enable people to learn without being aware of it happening.
C. They satisfy a need for people to compete with each other.
D. People learn a narrow range of skills but they are still useful
| Adam Martin, a lead programmer for an online games developer, says: “Computer games teach and people don’t even notice they’re being taught.” |
69. Which of the following does Steven Johnson disagree with?
A. The opinion that video games offer educational benefits to the user.
B. The attitude that video games are often labelled as predictable and undemanding.
C. The idea that children’s logic is tested more by video games than at school.
D. The suggestion that video games can be compared to scientific procedures.
| Games, he points out, generate satisfaction via the complexity of their virtual worlds, not by their robotic predictability. Testing the nature and limits of the laws of such imaginary worlds has more in common with scientific methods than with a pointless addiction, while the complexity of the problems children encounter within games exceeds that of anything they might find at school. |
70. Which of the following is the most suitable subtitle for the above reading passage?
A. Debate about the effects of video games on other forms of technology.
B. An examination of the opinions of young people about video games.
C. A discussion of whether attitudes towards video games are outdated.
D. An analysis of the principles behind the historical development of video games.
IV. WRITING
Part 1: Sentence transformation
A. Questions 71-80 (1.0 point)
Complete each restatement with the word given so that it has the same meaning as the original one. Do NOT change the form of the given word. You must use between TWO and SEVEN words, including the word given.
71. We got to work late because we decided to drive rather than take the train. (INSTEAD)
→ We got to work late because we decided to drive ____instead of taking______ the train.
| instead of + Ving: thay vì = rather than |
72. I cannot get all my clothes in the suitcase (BIG)
→ The suitcase__is not big enough to________ take all my clothes.
| be + adj + enough to do sth: đủ … để làm gì |
73. The earthquake made many people homeless. (LARGE)
→ The earthquake made___a large number of people_______ homeless.
| a large number of = many: nhiều (dùng cho danh từ đếm được) |
74. Tickets for the concert cannot be bought before 12th May. (SALE)
→ Tickets for the concert will not __be for sale until/before___ 12th May.
| be on/for sale: có sẵn để mua |
75. I really don’t want to go to work today. (FEEL)
→ I really __don’t feel like going_____________ to work today.
| feel like doing sth: cảm thấy thích/muốn làm gì |
76. I didn’t like Chemistry when I was at school. (USED)
→ I __used not to ________ like Chemistry when I was at school.
| used not to: từng không làm gì (trong quá khứ) |
77. “All your complaints will be investigated by my staff tomorrow,” said the bank manager. (LOOK)
→ The bank manager promised that his staff__would look into__ all our complaints the next day.
| look into: xem xét kỹ |
78. She has always been proud of her appearance. (PRIDED)
→ She has always _prided herself on________ her appearance.
| be proud of: tự hàotake pride in: tự hào vềpride yourself on something: tự hào với bản thân về cái gì |
79. The town hall has approved the plans for a new sports center. (GREEN)
→ The town hall __has given the green light to______ the plans for a new sports center.
| give the green light to sth: cho phép điều gì đó xảy ra |
80. She didn’t like the young man asking her so many questions (OBJECTED)
→ She __objected to being asked___ so many questions.
| object to sth: phản đối, chống lạiBị động: being + PII |
B. Questions 81 – 90 (1.0 point)
Finish each of the following sentences in such a way that it means exactly the same as the sentence printed before it. You MUST write the complete sentences.
81. I didn’t buy the camera because it was so expensive.
→ If the camera __hadn’t been so expensive, I would have bought the camera______.
| Câu điều kiện loại 3 diễn tả một điều kiện không có thực ở quá khứ:If + S + had + PII, S + would have + PII |
82. I have never had such a delicious meal.
→ It’s _the most delicious meal I’ve ever had_______.
| Thì hiện tại hoàn thành: It/This/That is the first/second/most/best/only/worst/… + S + have + PII |
83. “What an excellently organized office you have!” Mary said to David.
→ Mary complimented __David on his excellently organized office_____.
| compliment sb on sth: khen ngợi ai vì cái gì |
84. As soon as she said it, she burst into tears.
→ No sooner __had she said it than she burst into tears___.
| No sooner + had + S + PII + than S + V: Ngay khi |
85. It’s possible that they took the wrong road in the dark.
→ They might ___have taken the wrong road in the dark_____________________.
| might have + PII: một khả năng có thể đã xảy ra ở quá khứ |
86. Rosana found it difficult to persuade her boss to give her a pay rise.
→ Rosana had __great difficulty persuading her boss to give her a pay rise.____.
| find it difficult to do sth = have difficulty doing sth: gặp khó khăn khi làm gì |
87. They tried again to free the hostages.
→ Another effort __was made to free the hostages_____.
| make an effort to: cố gắng làm gìBị động: be + PII |
88. I would rather have the lesson on Wednesday than on Tuesday.
→ I would prefer _to have the lesson on Wednesday rather than on Tuesday__.
| S + Would rather + V + than + V: thà làm gì hơn làm gì= S + Would prefer + to + V + rather than + V: thà làm gì hơn làm gì |
89. Robert really enjoys making other people look stupid.
→ Robert really takes __an interest in making other people look stupid_________.
| enjoy = take an interest in: quan tâm đến cái gì |
90. I really must find time to clear out the attic.
→ I really must get _around to clear out the attic____________.
| find time = get around to sth: tìm thời gian để làm điều gì đó mà bạn đã dự định hoặc muốn làm |
Part 2. Composition (1.0 point)
Write a paragraph of about 150 words on the following topic:
Many people believe that it is important for teenagers to make decisions about matters that affect them (such as food, clothes, entertainment, learning, etc.).
To what extent do you agree or disagree with this statement? Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own knowledge and experience.
– END OF THE TEST –
B. Link tải về Đề thi Vào 10 Chuyên Anh Đồng Nai 2021-2022
| BẠN CÓ THỂ TẢI VỀ TẠI: |
| Đề bài: link Đáp án + Phân tích: link |